↓↓下拉很多 ➟➟微信☎
产品3d渲染制作:
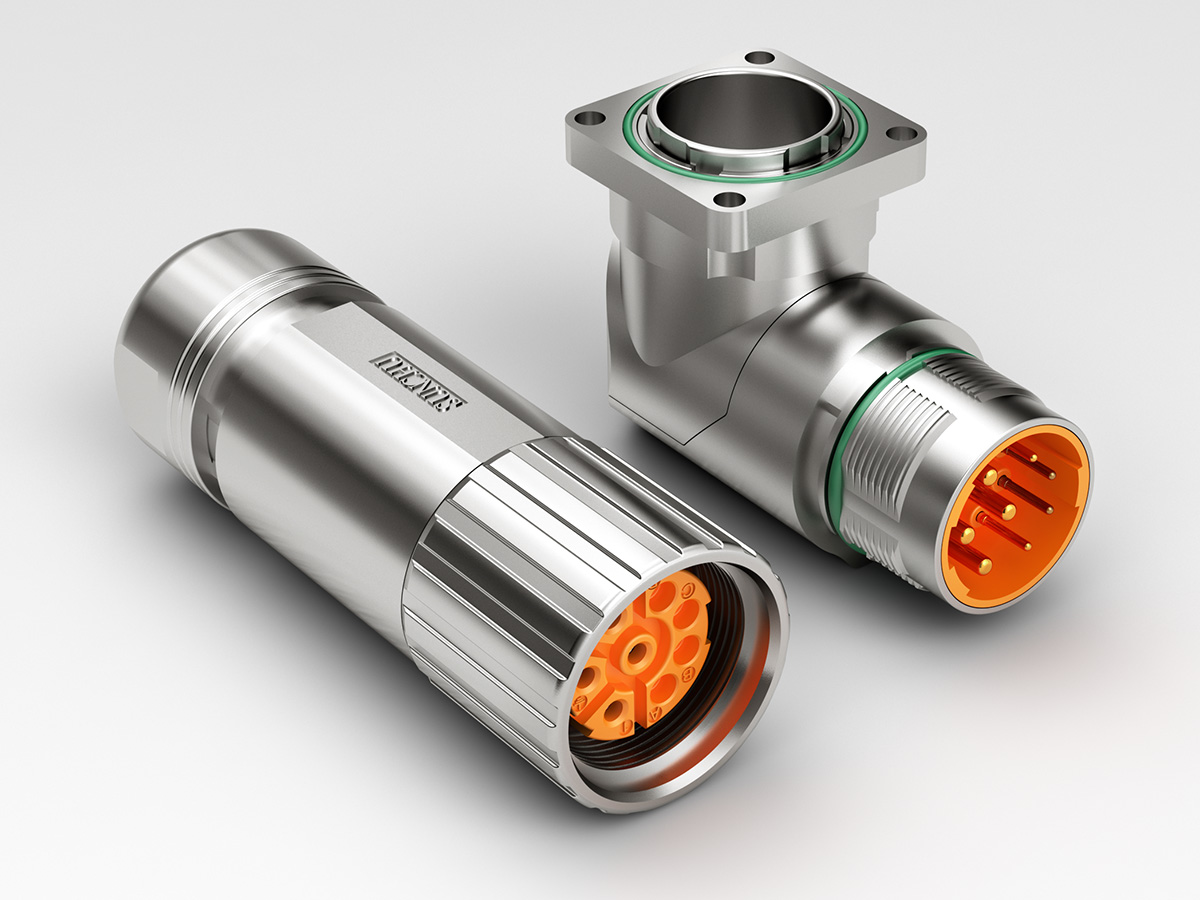
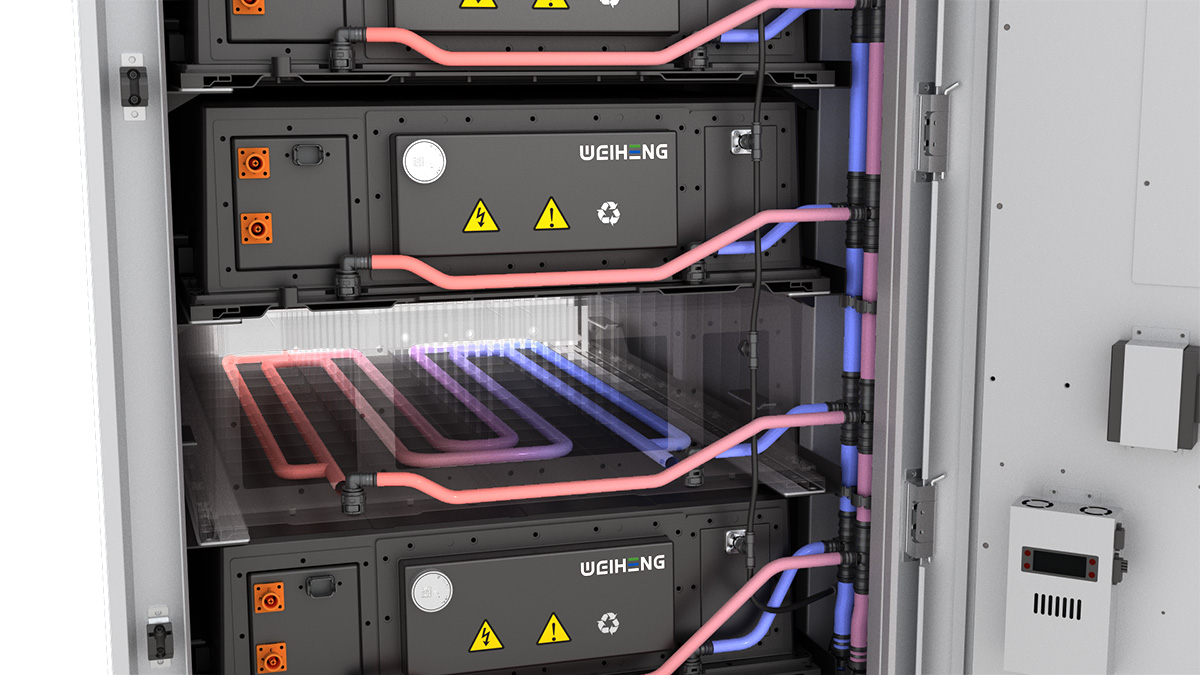
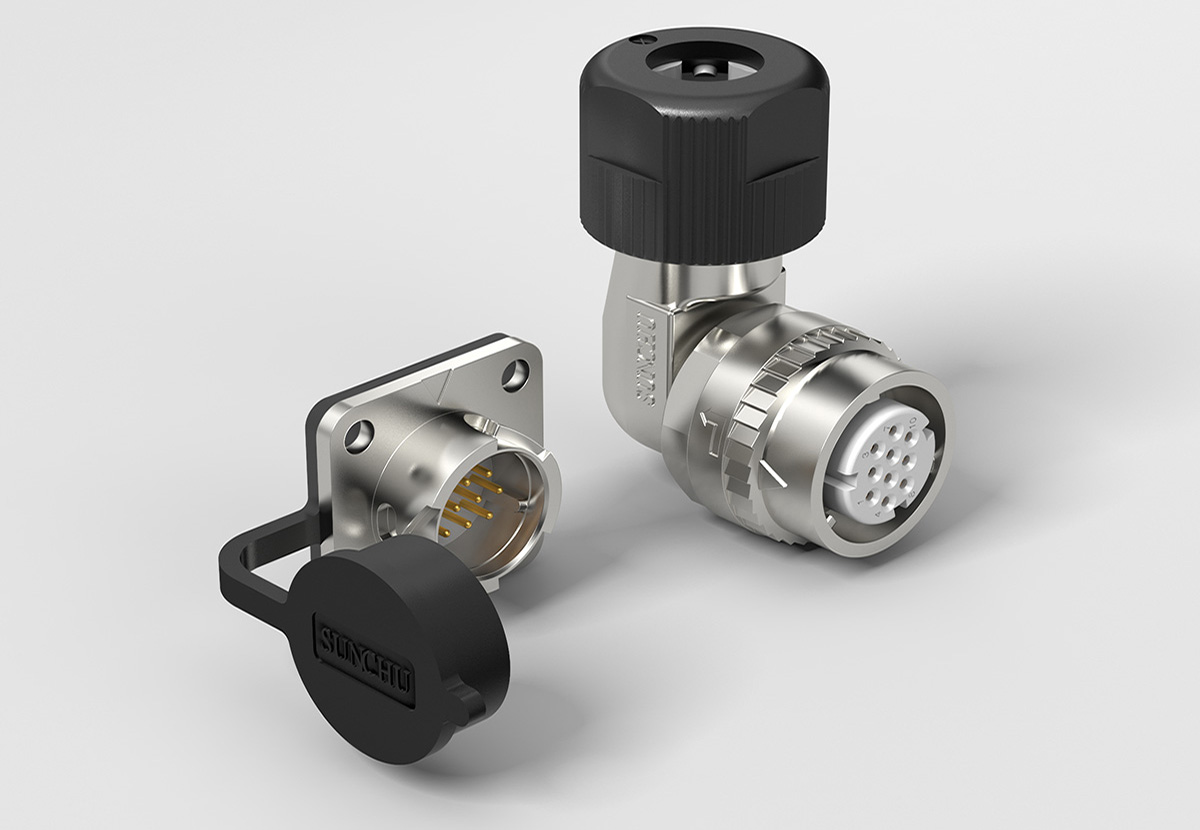
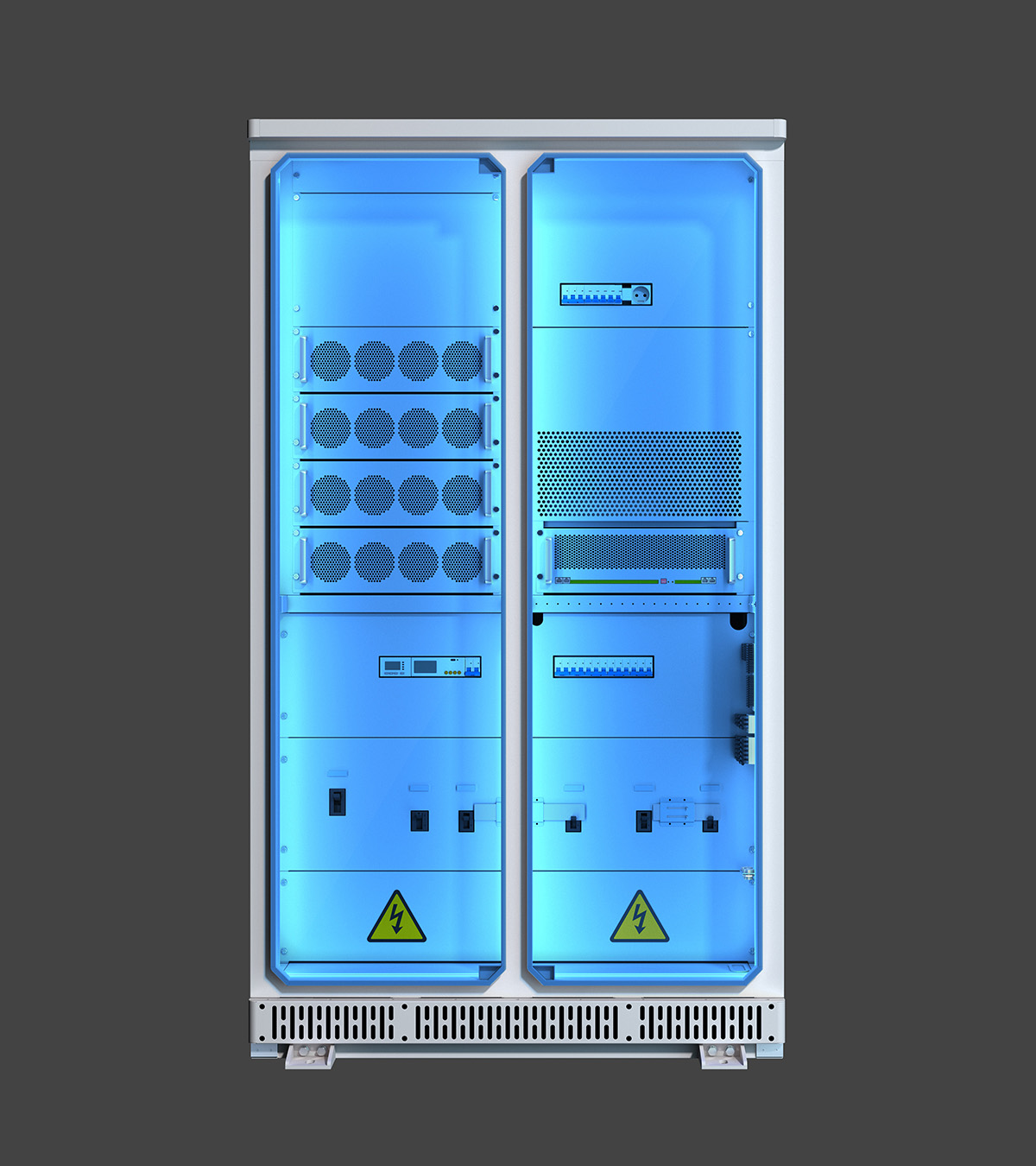





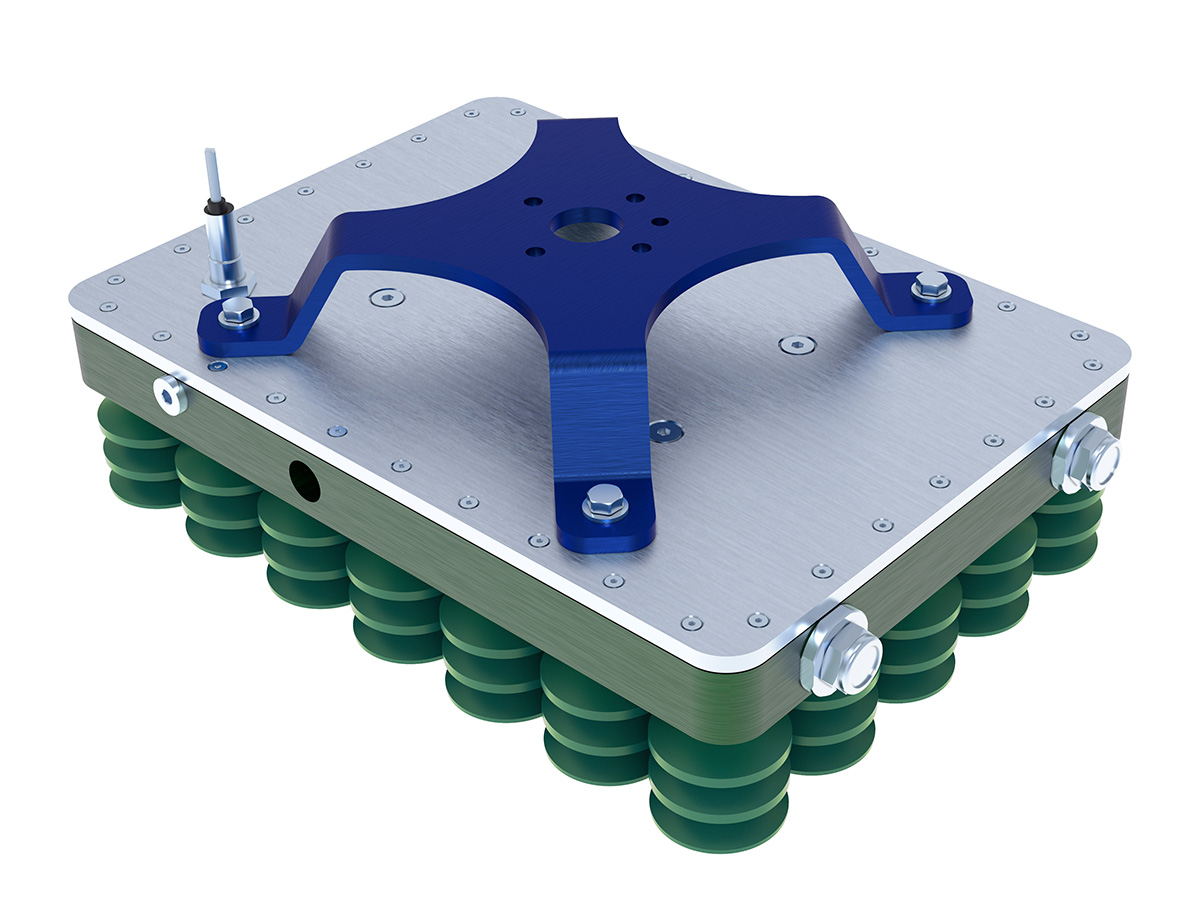

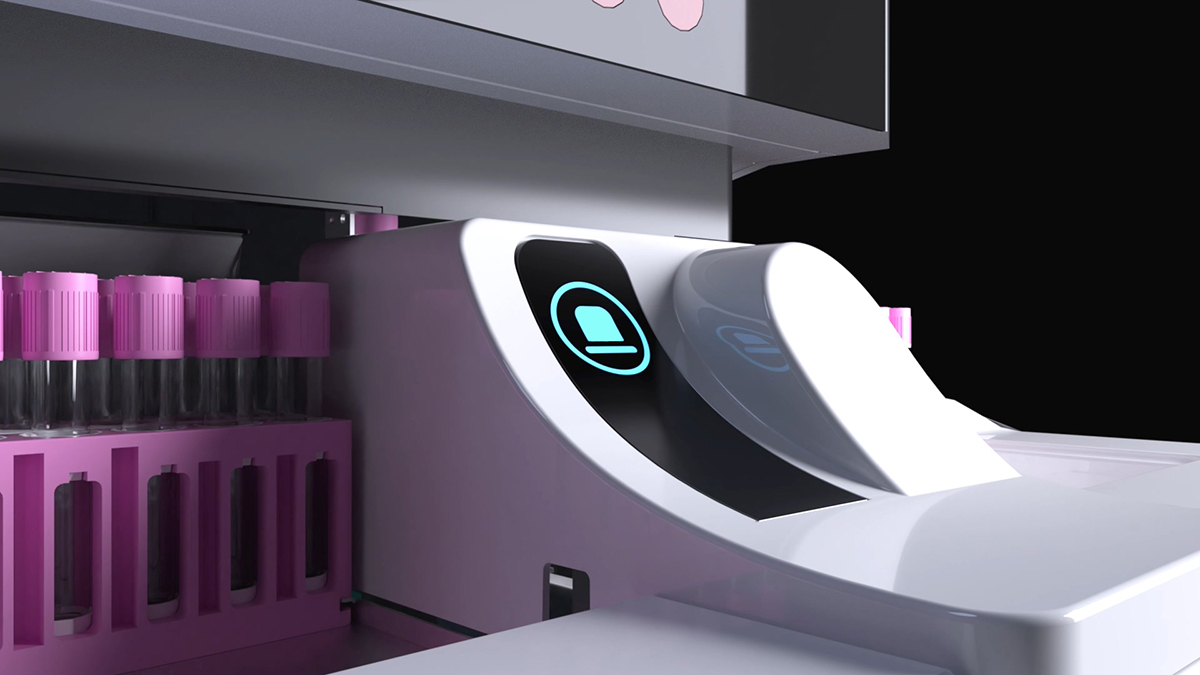



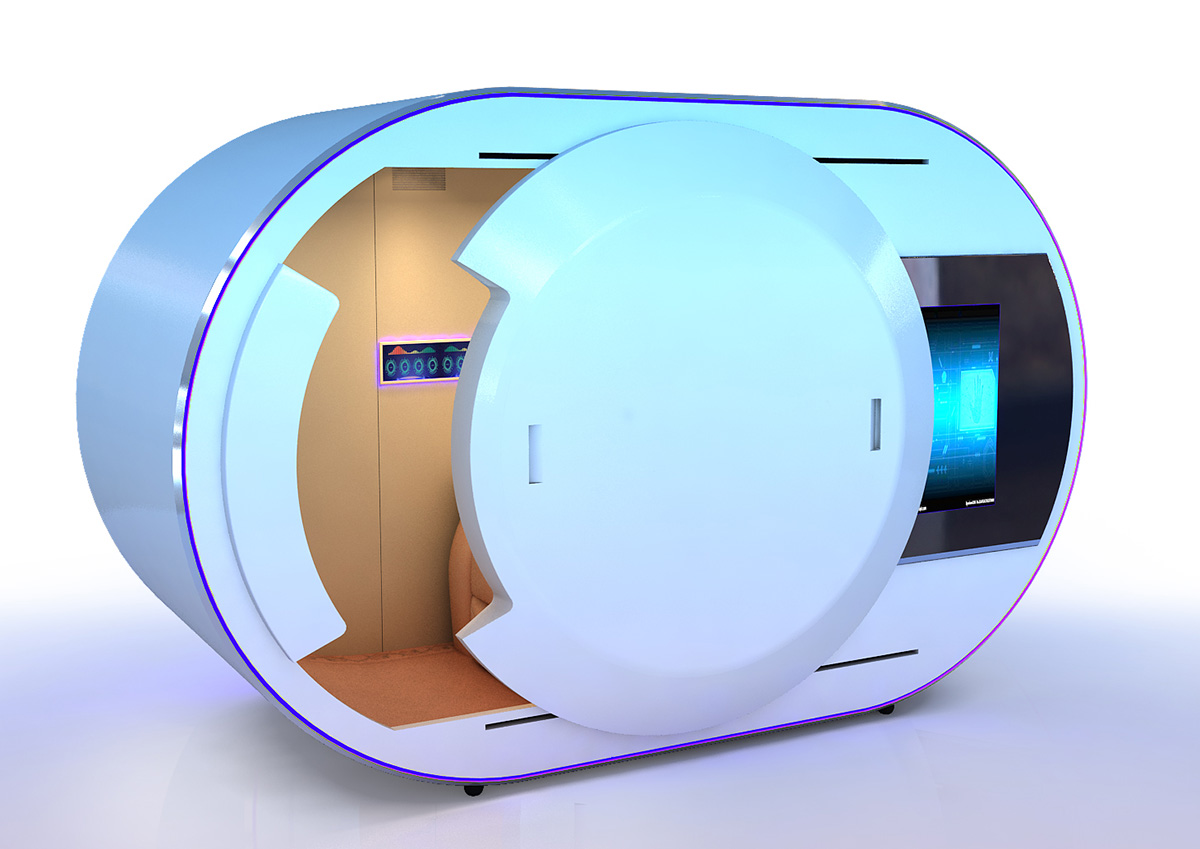


企业产品的3D渲染可根据应用场景、技术手段和目标需求分为以下主要类别,各分类在功能、用途和技术实现上具有显著差异:
一、按应用场景分类
产品营销渲染
核心用途:用于广告宣传、电商展示、展会演示等商业场景。
技术特点:追求视觉冲击力,通过超写实材质、光影效果和动态展示(如旋转、拆解)突出产品卖点。
示例:手机广告中的透明材质渲染、汽车广告的动态光线追踪。
工业设计渲染
核心用途:辅助产品设计验证、工程评估和制造流程优化。
技术特点:注重结构精度、尺寸标注和装配关系,需与CAD数据无缝对接。
示例:机械零件渲染中的公差标注、汽车内饰的工程级材质模拟。
建筑与空间渲染
核心用途:展示建筑外观、室内布局或城市规划方案。
技术特点:强调场景氛围营造,需结合环境光照、植被模拟和人流动态。
示例:房地产项目的虚拟样板房、城市规划的3D沙盘演示。
医疗与科研渲染
核心用途:医学教育、手术模拟或生物分子结构可视化。
技术特点:需高精度解剖模型和科学数据支持,符合医学行业标准。
示例:心脏三维重建、病毒蛋白结构的动态模拟。
二、按技术手段分类
静态渲染
核心特点:生成单帧高质量图像,适用于广告海报、产品手册等。
技术实现:通过光线追踪、全局光照算法实现超写实效果。
示例:高端化妆品的瓶身材质渲染、珠宝广告的钻石反光效果。
动态渲染(动画)
核心特点:生成连续帧序列,用于产品演示视频或交互式体验。
技术实现:结合骨骼动画、粒子系统和动力学模拟。
示例:汽车碰撞测试动画、机械臂装配流程演示。
实时渲染
核心特点:通过游戏引擎(如Unity、Unreal)实现低延迟交互。
技术实现:采用简化算法和硬件加速,支持实时调整视角和材质。
示例:虚拟现实(VR)产品展示、AR设备交互演示。
交互式渲染
核心特点:用户可通过输入设备(如鼠标、触控屏)动态修改渲染参数。
技术实现:结合WebGL、Three.js等前端技术实现网页端交互。
示例:在线产品配置器(如定制家具颜色、材质)、3D产品目录浏览。
三、按目标需求分类
写实风格渲染
核心目标:还原产品真实外观和物理特性。
技术要点:精确模拟材质反射、折射和纹理细节。
示例:食品包装的透明质感渲染、金属产品的氧化层模拟。
风格化渲染
核心目标:通过艺术化处理强化品牌调性或情感表达。
技术要点:采用卡通着色、低多边形建模或非真实感渲染(NPR)。
示例:儿童玩具的卡通化渲染、复古风格产品的手绘质感。
数据可视化渲染
核心目标:将抽象数据转化为直观的3D图形。
技术要点:结合图表算法和动态交互,支持多维数据展示。
示例:气象数据的三维云图、工业设备的温度场分布模拟。
四、按行业细分分类
消费电子
典型需求:手机、电脑等产品的外观渲染和内部结构拆解。
技术重点:超薄材质模拟、动态UI界面展示。
汽车制造
典型需求:车身流线设计、内饰材质对比和碰撞测试模拟。
技术重点:大规模场景渲染、动力学模拟。
家居建材
典型需求:家具的材质纹理、空间布局搭配和光照效果。
技术重点:环境光遮蔽(AO)、全局光照(GI)优化。
医疗器械
典型需求:手术器械的精密结构、医学影像的三维重建。
技术重点:高精度建模、医学数据兼容性。
五、关键技术趋势
AI辅助渲染
应用场景:自动材质生成、降噪优化和初步场景布局。
示例:NVIDIA Omniverse中的AI去噪技术。
云渲染服务
应用场景:大规模动画渲染、实时协作设计。
示例:Fox Renderfarm的分布式渲染集群。
跨平台兼容性
应用场景:支持PC、移动端和VR设备的统一渲染流程。
示例:Unity的通用渲染管线(URP)。
结论:分类的实践意义
企业产品的3D渲染分类直接关联技术选型、成本预算和交付周期。例如:
广告营销需优先选择写实风格渲染和动态动画,以提升视觉吸引力;
工业设计需侧重工程级渲染和实时交互,以优化设计流程;
医疗科研需依赖高精度渲染和数据兼容性,以支持科学验证。
通过精准分类,企业可高效匹配技术资源,实现产品价值最大化。
关于对3D渲染专业的理解与分析
一、专业定义与核心价值
3D渲染专业是计算机图形学与数字艺术交叉的领域,通过技术手段将虚拟三维模型转化为可视化图像或动画。其核心价值体现在:
突破物理限制:在虚拟空间中实现现实难以复现的场景(如爆炸特效、微观粒子运动)。
提升设计效率:通过实时渲染技术(如Unreal Engine)实现“设计-修改-验证”一体化,缩短产品开发周期。
降低商业成本:用虚拟渲染替代实物拍摄(如汽车广告中的虚拟场景),节省拍摄、运输等费用。
类比:3D渲染如同“数字摄影师”,通过调整光线、材质和视角,将虚拟模型转化为具有商业价值的视觉内容。
二、专业核心技能与知识体系
3D渲染专业需掌握以下技能模块,形成技术闭环:
技能模块 具体内容 技术工具示例
三维建模 基于几何学原理构建虚拟模型,包括多边形建模、曲面建模等。 Maya、3ds Max、Blender
材质与纹理 通过算法模拟真实材质的物理特性(如金属反光、布料褶皱)。 Substance Painter、Quixel Mixer
光照与渲染算法 掌握全局光照、光线追踪、路径追踪等算法,优化渲染效率与画质。 V-Ray、Arnold、Octane Render
动画与动力学 为模型添加骨骼绑定、粒子特效和物理模拟(如流体、布料运动)。 Houdini、After Effects、Nvidia Flex
实时渲染引擎 使用游戏引擎实现低延迟交互,支持VR/AR设备。 Unity、Unreal Engine
后期合成 将渲染元素与实拍画面或UI界面融合,调整色彩与光影。 Nuke、Adobe Premiere、DaVinci Resolve
技能逻辑:建模是基础,材质与光照决定真实感,动画赋予生命力,实时引擎拓展应用场景,后期合成提升最终质量。
三、行业应用与需求分析
3D渲染专业已渗透至多个行业,形成差异化需求:
行业领域 核心需求 典型案例
影视动画 超写实特效、角色动画、场景渲染。 《阿凡达》中的虚拟生物、《流浪地球》的太空站场景。
游戏开发 实时渲染优化、角色动作设计、场景加载效率。 《原神》的开放世界渲染、《赛博朋克2077》的动态光照系统。
建筑可视化 虚拟样板房、城市规划沙盘、施工流程模拟。 碧桂园的VR看房系统、新加坡滨海湾花园的3D规划演示。
工业设计 产品结构验证、工程级材质模拟、装配动画。 特斯拉Model 3的内部结构渲染、波音飞机的虚拟装配流程。
医疗教育 解剖模型重建、手术模拟、分子结构可视化。 虚拟心脏手术培训系统、新冠病毒蛋白结构的3D演示。
需求趋势:
影视与游戏:追求实时渲染与AI辅助设计(如NVIDIA Omniverse的AI去噪)。
建筑与工业:强调云渲染协作(如Fox Renderfarm)与轻量化交付(WebGL格式)。
医疗与教育:依赖高精度建模与交互式学习(如VR解剖实验室)。
四、职业发展路径与薪资前景
3D渲染专业的职业发展呈现“技术纵深+领域跨界”双重特征:
技术纵深路径
初级渲染师:负责基础材质调试与场景搭建,月薪8K-12K。
中级特效师:主导技能特效设计与性能优化,年薪24W-40W。
高级技术总监:统筹渲染管线架构与跨部门协作,年薪50W-100W。
领域跨界路径
影视特效总监:需掌握故事板设计与镜头语言,年薪80W+。
游戏引擎工程师:需精通C++与Shader编程,年薪60W+。
医疗3D建模师:需具备医学知识背景,年薪40W+。
薪资数据(以一线城市为例):
初级岗位:平均月薪10K,3年经验后涨幅达150%。
高级岗位:年薪50W-100W,技术专家可突破200W(如参与《黑神话:悟空》特效团队)。
行业供需:
2025年,北上广深单日新增“UE特效”岗位超200个,而传统3D模型岗位仅为80个左右,技术稀缺性显著。
五、技术挑战与未来趋势
当前挑战
硬件限制:实时渲染需高性能GPU支持,移动端设备适配难度大。
数据安全:云渲染平台存在数据泄露风险,需加强加密技术。
AI伦理:AI生成内容的版权界定与训练数据合规性争议。
未来趋势
“端云协同”:本地终端预览+云端AI集群渲染,实现“电影级质量、手游级速度”。
“人机共创”:AI承担技术性工作(如降噪、场景分析),人类专注创意决策。
全球化与出海:国产游戏(如《原神》)推动企业招聘国际化特效师,要求多语言UI适配。
六、结论:3D渲染专业的核心价值与建议
核心价值:
3D渲染专业是数字时代的“视觉翻译官”,将抽象数据转化为直观的商业内容,连接技术、艺术与商业需求。
学习建议:
技术基础:优先掌握Blender(免费开源)或Maya(行业主流)建模工具。
实战项目:通过Kaggle或ArtStation参与虚拟场景渲染竞赛,积累作品集。
跨领域学习:结合游戏引擎(如Unity)或医疗软件(如3D Slicer)拓展应用场景。
行业展望:
随着元宇宙、数字孪生等技术的普及,3D渲染专业将成为“数字基建”的核心组成部分,从业者需持续关注实时渲染、AI辅助设计与云协作三大方向。
3D渲染制作凭借其技术优势与行业需求增长,已成为数字创意领域的关键驱动力,其核心优势与未来前景体现在以下五个维度:
一、技术核心优势:突破物理限制,实现视觉革命
超写实画质
通过光线追踪、全局光照等算法,3D渲染可模拟真实光影效果,实现毫米级精度建模。例如在影视特效中,虚拟场景与实拍画面无缝融合;在工业设计领域,产品渲染图可精准呈现材质纹理与动态光影,替代传统实物拍摄。
高效流程优化
实时渲染技术(如Unreal Engine 5的Nanite虚拟微多边形几何体系统)支持设计师在引擎内直接调整模型与材质,实现“设计-渲染-修改”一体化。云渲染平台(如炫云)通过分布式计算,将复杂动画渲染时间从数日压缩至数小时,显著提升项目交付效率。
跨领域应用兼容性
3D渲染技术已渗透至影视、游戏、建筑、医疗、教育等多个行业。例如在医疗领域,3D渲染用于手术模拟与器官建模;在教育领域,通过虚拟实验室实现沉浸式教学。这种技术普适性使其成为数字化时代的“通用语言”。
二、行业需求驱动:市场规模与政策红利双重加持
市场规模爆发式增长
影视与游戏行业:2025年全球3D动画电影市场规模预计突破47亿美元,中国3D动画电影票房年增长率达19.97%。《黑神话:悟空》等游戏通过3D毛发渲染与粒子特效引发全球热议,推动技术迭代。
建筑与工业设计:云渲染市场规模年增长率超25%,设计师通过云端协作实现跨国项目实时渲染,降低硬件成本70%以上。
政策与技术双重赋能
中国将游戏产业列为“数字创意产业”核心领域,出台《网络出版科技创新引领计划》,推动VR/AR、云游戏等前沿技术研发。
AI辅助设计工具(如Stable Diffusion、Kaiber)普及,降低3D渲染技术门槛,催生更多细分岗位需求。
三、职业前景分析:高薪资与多元化发展路径
人才缺口与薪资竞争力
3D渲染师平均月薪达15K以上,高级特效师年薪可达50W-100W。例如在广州天河区,特效师平均月薪达23.8K;深圳南山区的次世代特效师年薪突破80W。
行业供需失衡加剧:2025年北上广深单日新增“UE特效”岗位超200个,而传统3D模型岗位仅为80个左右。
职业晋升通道清晰
初级阶段:负责基础粒子效果与材质调试,月薪8K-12K。
中级阶段:主导技能特效设计与性能优化,年薪24W-40W。
高级阶段:统筹特效系统架构与跨部门协作,年薪50W-100W。
创业路径:凭借技术积累开发独立游戏或特效外包公司,如《饥荒》式2.5D国风端游的爆款案例。
四、未来趋势:技术融合与全球化布局
“端云协同”与“人机共创”
本地终端负责快速预览,云端AI集群处理最终渲染,实现“电影级质量、手游级速度”。
AI承担技术性工作(如降噪、场景分析),人类专注创意决策,提升生产效率。
全球化与出海战略
国产游戏(如《原神》《崩坏:星穹铁道》)全球热销,推动企业招聘国际化特效师,要求掌握多语言UI设计与本地化美术风格适配。
东南亚、中东成为新兴增长极,特效师需兼顾文化差异与视觉冲击力。
五、挑战与机遇并存:技术伦理与行业规范
技术伦理问题
AI生成内容的版权界定、训练数据的合规性亟待解决。例如,渲染生成的虚拟角色形象可能涉及肖像权争议。
行业规范升级
国家广播电视总局对网络剧片发放行政许可,推动3D动画行业规范化发展。例如,网络动画需通过内容审核,实现社会效益与市场价值的统一。
结论:3D渲染制作——数字时代的“新基建”
3D渲染制作不仅是技术工具,更是推动产业升级的核心引擎。其优势体现在技术突破性、行业普适性、职业高价值性三大层面,未来将深度融入元宇宙、数字孪生等前沿领域,成为连接虚拟与现实的桥梁。对于从业者而言,掌握3D渲染技术不仅是职业发展的“金钥匙”,更是参与数字文明建设的“入场券”。
The 3D rendering of enterprise products can be classified into the following main categories based on application scenarios, technical means, and target requirements, each with significant differences in functionality, purpose, and technical implementation:
1、 Classified by application scenario
Product marketing rendering
Core use: Used for commercial scenarios such as advertising promotion, e-commerce display, exhibition demonstrations, etc.
Technical features: Pursuing visual impact, highlighting product selling points through hyper realistic materials, light and shadow effects, and dynamic displays such as rotation and disassembly.
Example: Transparent material rendering in mobile advertising, dynamic ray tracing in car advertising.
Industrial design rendering
Core purpose: To assist in product design verification, engineering evaluation, and manufacturing process optimization.
Technical features: Emphasis is placed on structural accuracy, dimensional annotation, and assembly relationships, requiring seamless integration with CAD data.
Example: Tolerance annotation in mechanical parts rendering, engineering grade material simulation of automotive interiors.
Architecture and Space Rendering
Core purpose: To showcase the exterior appearance, interior layout, or urban planning schemes of buildings.
Technical features: Emphasizing the creation of scene atmosphere, it is necessary to combine environmental lighting, vegetation simulation, and pedestrian flow dynamics.
Example: Virtual model houses for real estate projects, 3D sand table demonstrations for urban planning.
Medical and scientific research rendering
Core applications: Medical education, surgical simulation, or visualization of biological molecular structures.
Technical features: Requires high-precision anatomical models and scientific data support, in line with medical industry standards.
Example: Three dimensional reconstruction of the heart, dynamic simulation of viral protein structure.
2、 Classified by technical means
Static rendering
Core feature: Generate high-quality single frame images, suitable for advertising posters, product manuals, etc.
Technical implementation: Achieve hyper realistic effects through ray tracing and global lighting algorithms.
Example: Rendering of bottle materials for high-end cosmetics, diamond reflective effect for jewelry advertisements.
Dynamic rendering (animation)
Core feature: Generate continuous frame sequences for product demonstration videos or interactive experiences.
Technical implementation: Combining skeletal animation, particle systems, and dynamic simulation.
Example: Car collision test animation, demonstration of robotic arm assembly process.
Real time rendering
Core feature: Low latency interaction achieved through game engines such as Unity and Unreal.
Technical implementation: Adopting simplified algorithms and hardware acceleration, supporting real-time adjustment of viewing angles and materials.
Example: Virtual Reality (VR) product display, AR device interactive demonstration.
Interactive rendering
Core feature: Users can dynamically modify rendering parameters through input devices such as mice and touch screens.
Technical implementation: Combining front-end technologies such as WebGL and Three.js to achieve web-based interaction.
Example: Online product configurator (such as customizing furniture colors and materials), 3D product catalog browsing.
3、 Classify by target requirements
Realistic style rendering
Core objective: To restore the true appearance and physical characteristics of the product.
Technical key points: Accurately simulate material reflection, refraction, and texture details.
Example: Transparent texture rendering of food packaging, simulation of oxide layer on metal products.
Stylized rendering
Core objective: To enhance brand tone or emotional expression through artistic processing.
Technical points: Adopt cartoon coloring, low polygon modeling, or non realistic rendering (NPR).
Example: Cartoon rendering of children's toys, hand drawn texture of retro style products.
Data visualization rendering
Core objective: Transform abstract data into intuitive 3D graphics.
Technical points: Combining chart algorithms and dynamic interaction, supporting multi-dimensional data display.
Example: Three dimensional cloud maps of meteorological data, simulation of temperature field distribution of industrial equipment.
4、 Classified by industry segmentation
Consumer Electronics
Typical requirements: Rendering the appearance and dismantling the internal structure of products such as mobile phones and computers.
Technical focus: Ultra thin material simulation, dynamic UI interface display.
Automobile manufacturing
Typical requirements: body streamline design, interior material comparison, and collision testing simulation.
Technical focus: large-scale scene rendering, dynamic simulation.
Home building materials
Typical requirements: Material texture, spatial layout matching, and lighting effect of furniture.
Technical focus: Optimization of ambient occlusion (AO) and global illumination (GI).
Medical devices
Typical requirements: Precision structure of surgical instruments, 3D reconstruction of medical images.
Technical focus: high-precision modeling, medical data compatibility.
5、 Key technology trends
AI assisted rendering
Application scenarios: automatic material generation, noise reduction optimization, and preliminary scene layout.
Example: AI denoising technology in NVIDIA Omniverse.
Cloud rendering service
Application scenarios: Large scale animation rendering, real-time collaborative design.
Example: Distributed rendering cluster of Fox Renderfarm.
Cross platform compatibility
Application scenario: Supports a unified rendering process for PC, mobile, and VR devices.
Example: Unity's Universal Rendering Pipeline (URP).
Conclusion: The practical significance of classification
The 3D rendering classification of enterprise products is directly related to technology selection, cost budget, and delivery cycle. For example:
Advertising and marketing should prioritize realistic style rendering and dynamic animation to enhance visual appeal;
Industrial design should focus on engineering level rendering and real-time interaction to optimize the design process;
Medical research relies on high-precision rendering and data compatibility to support scientific validation.
Through precise classification, enterprises can efficiently match technical resources and maximize product value.
Understanding and Analysis of 3D Rendering Specialty
1、 Professional Definition and Core Values
3D rendering is a field that intersects computer graphics and digital art, where virtual 3D models are transformed into visual images or animations through technological means. Its core values are reflected in:
Breaking through physical limitations: Achieving scenes in virtual space that are difficult to reproduce in reality, such as explosion effects and microscopic particle motion.
Improve design efficiency: By using real-time rendering technology (such as Unreal Engine) to achieve the integration of "design modification verification", the product development cycle can be shortened.
Reduce business costs: Replace physical shooting with virtual rendering (such as virtual scenes in car advertising), saving costs such as shooting and transportation.
Analogy: 3D rendering is like a 'digital photographer', transforming virtual models into commercially valuable visual content by adjusting lighting, materials, and perspectives.
2、 Professional core skills and knowledge system
The 3D rendering profession requires mastery of the following skill modules to form a technical closed loop:
Specific content of skill module and examples of technical tools
3D modeling is based on geometric principles to construct virtual models, including polygon modeling, surface modeling, etc. Maya、3ds Max、Blender
Materials and textures simulate the physical properties of real materials through algorithms, such as metal reflections and fabric wrinkles. Substance Painter、Quixel Mixer
Mastering global lighting, ray tracing, path tracing, and other algorithms in lighting and rendering, optimizing rendering efficiency and image quality. V-Ray、Arnold、Octane Render
Animation and dynamics add bone binding, particle effects, and physical simulations (such as fluid and fabric motion) to the model. Houdini、After Effects、Nvidia Flex
The real-time rendering engine uses a game engine to achieve low latency interaction and supports VR/AR devices. Unity、Unreal Engine
Post production synthesis integrates rendered elements with real-life footage or UI interfaces, adjusting colors and lighting. Nuke、Adobe Premiere、DaVinci Resolve
Skill logic: Modeling is the foundation, materials and lighting determine realism, animation gives vitality, real-time engine expands application scenarios, and post synthesis improves final quality.
3、 Industry application and demand analysis
The 3D rendering profession has penetrated into multiple industries, forming differentiated demands:
Typical Cases of Core Requirements in Industry Fields
Super realistic special effects, character animation, and scene rendering in film and television animation. Virtual creatures in Avatar and space station scenes in Wandering Earth.
Real time rendering optimization for game development, character action design, and scene loading efficiency. The open world rendering of Genshin Impact and the dynamic lighting system of Cyberpunk 2077.
Architectural visualization virtual model house, urban planning sand table, construction process simulation. VR viewing system of Country Garden and 3D planning demonstration of Marina Bay Gardens in Singapore.
Industrial design product structure verification, engineering grade material simulation, assembly animation. The internal structure rendering of Tesla Model 3 and the virtual assembly process of Boeing aircraft.
Medical education anatomy model reconstruction, surgical simulation, molecular structure visualization. Virtual heart surgery training system, 3D demonstration of COVID-19 protein structure.
Demand trend:
Film and gaming: Pursuing real-time rendering and AI assisted design (such as NVIDIA Omniverse's AI denoising).
Architecture and Industry: Emphasize cloud rendering collaboration (such as Fox Renderfarm) and lightweight delivery (WebGL format).
Healthcare and education: rely on high-precision modeling and interactive learning (such as VR anatomy laboratories).
4、 Career Development Path and Salary Prospects
The career development of 3D rendering profession presents a dual feature of "technical depth+cross domain":
Technical depth path
Junior renderer: responsible for basic material debugging and scene construction, with a monthly salary of 8K-12K.
Intermediate Special Effects Specialist: Leading skills in special effects design and performance optimization, with an annual salary of 24W-40W.
Senior Technical Director: Responsible for coordinating rendering pipeline architecture and cross departmental collaboration, with an annual salary of 50W-100W.
Cross disciplinary path in the field
Film and Television Special Effects Director: Must master storyboard design and camera language, with an annual salary of over 80W.
Game Engine Engineer: Proficient in C++and Shader programming, with an annual salary of over 60W.
Medical 3D modeler: Must have a medical knowledge background and an annual salary of over 40W.
Salary data (taking first tier cities as an example):
Junior position: Average monthly salary of 10K, with a 150% increase after 3 years of experience.
Senior positions: Annual salary of 50W-100W, technical experts can exceed 200W (such as participating in the special effects team of "Black Myth: Wukong").
Industry supply and demand:
By 2025, Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen will add over 200 "UE special effects" positions in a single day, while traditional 3D modeling positions will only be around 80, indicating significant technological scarcity.
5、 Technological Challenges and Future Trends
Current challenges
Hardware limitations: Real time rendering requires high-performance GPU support, making it difficult to adapt to mobile devices.
Data security: There is a risk of data leakage in cloud rendering platforms, and encryption technology needs to be strengthened.
AI Ethics: Copyright Definition of AI Generated Content and Controversy over Training Data Compliance.
Future Trends
End cloud collaboration ": Local terminal preview+cloud AI cluster rendering, achieving" movie quality, mobile game speed ".
Human machine co creation ": AI undertakes technical tasks such as noise reduction and scene analysis, while humans focus on creative decision-making.
Globalization and sailing: domestic games (such as Genshin Impact) promote enterprises to recruit international special effects masters, requiring multilingual UI adaptation.
6、 Conclusion: Core values and recommendations of 3D rendering profession
Core values:
The 3D rendering profession is the "visual translator" of the digital age, transforming abstract data into intuitive commercial content, connecting technology, art, and business needs.
Learning advice:
Technical foundation: Prioritize mastering Blender (free and open-source) or Maya (mainstream industry) modeling tools.
Practical project: Participate in virtual scene rendering competitions through Kaggle or ArtStation to accumulate a portfolio of works.
Cross disciplinary learning: combining game engines (such as Unity) or medical software (such as 3D Slicer) to expand application scenarios.
Industry outlook:
With the popularization of technologies such as metaverse and digital twins, 3D rendering will become a core component of "digital infrastructure", and practitioners need to continue to pay attention to the three directions of real-time rendering, AI assisted design, and cloud collaboration.
3D rendering production, with its technological advantages and industry demand growth, has become a key driving force in the field of digital creativity. Its core advantages and future prospects are reflected in the following five dimensions:
1、 Core technological advantage: Breaking through physical limitations and achieving visual revolution
Super realistic picture quality
Through algorithms such as ray tracing and global illumination, 3D rendering can simulate real light and shadow effects, achieving millimeter level precision modeling. For example, in film and television special effects, virtual scenes seamlessly integrate with real footage; In the field of industrial design, product renderings can accurately present material textures and dynamic light and shadow, replacing traditional physical photography.
Efficient process optimization
Real time rendering technology, such as the Nanite virtual micro polygon geometry system in Unreal Engine 5, supports designers to directly adjust models and materials within the engine, achieving the integration of "design rendering modification". Cloud rendering platforms (such as Xuanyun) compress the rendering time of complex animations from a few days to several hours through distributed computing, significantly improving project delivery efficiency.
Cross domain application compatibility
3D rendering technology has penetrated into multiple industries such as film and television, gaming, architecture, healthcare, and education. For example, in the medical field, 3D rendering is used for surgical simulation and organ modeling; In the field of education, immersive teaching is achieved through virtual laboratories. The universality of this technology makes it the "universal language" of the digital age.
2、 Industry demand driven: dual support of market size and policy dividends
Explosive growth in market size
The film and gaming industry: The global 3D animation film market is expected to exceed $4.7 billion by 2025, with an annual box office growth rate of 19.97% for Chinese 3D animation films. Games such as "Black Myth: Wukong" have sparked global discussions and driven technological iteration through 3D fur rendering and particle effects.
Architecture and Industrial Design: The annual growth rate of the cloud rendering market exceeds 25%, and designers achieve real-time rendering of cross-border projects through cloud collaboration, reducing hardware costs by more than 70%.
Dual empowerment of policies and technology
China has listed the gaming industry as a core area of "digital creative industry" and introduced the "Network Publishing Technology Innovation Leading Plan" to promote VR/A



